Sensing pathogens
My group mainly focuses on how enteric bacterial pathogens are detected by human cells.
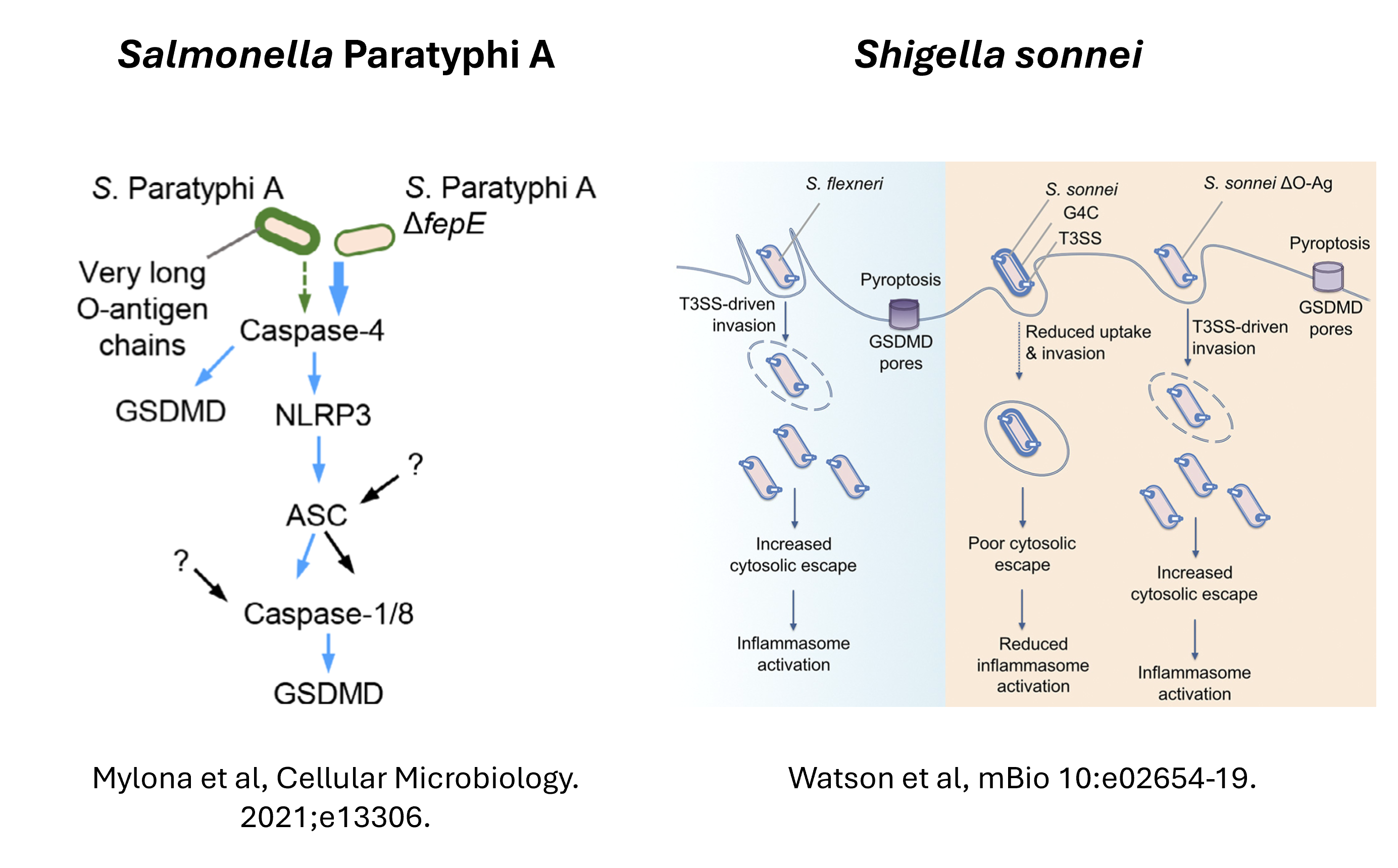
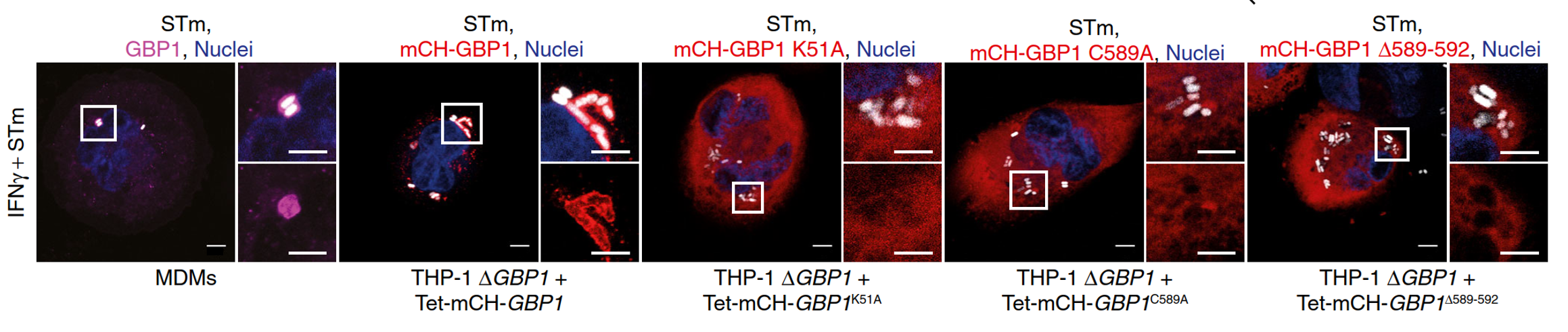
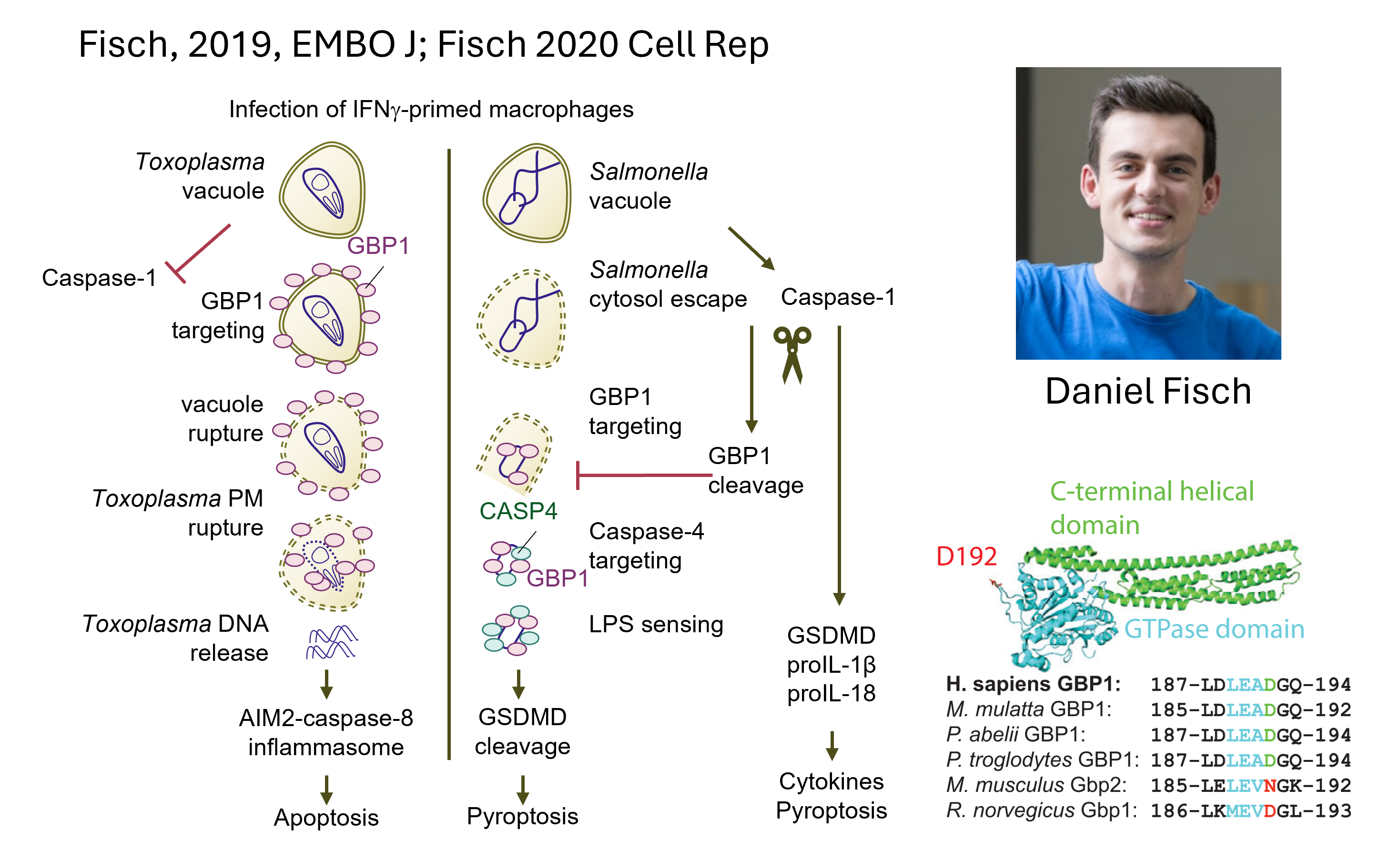
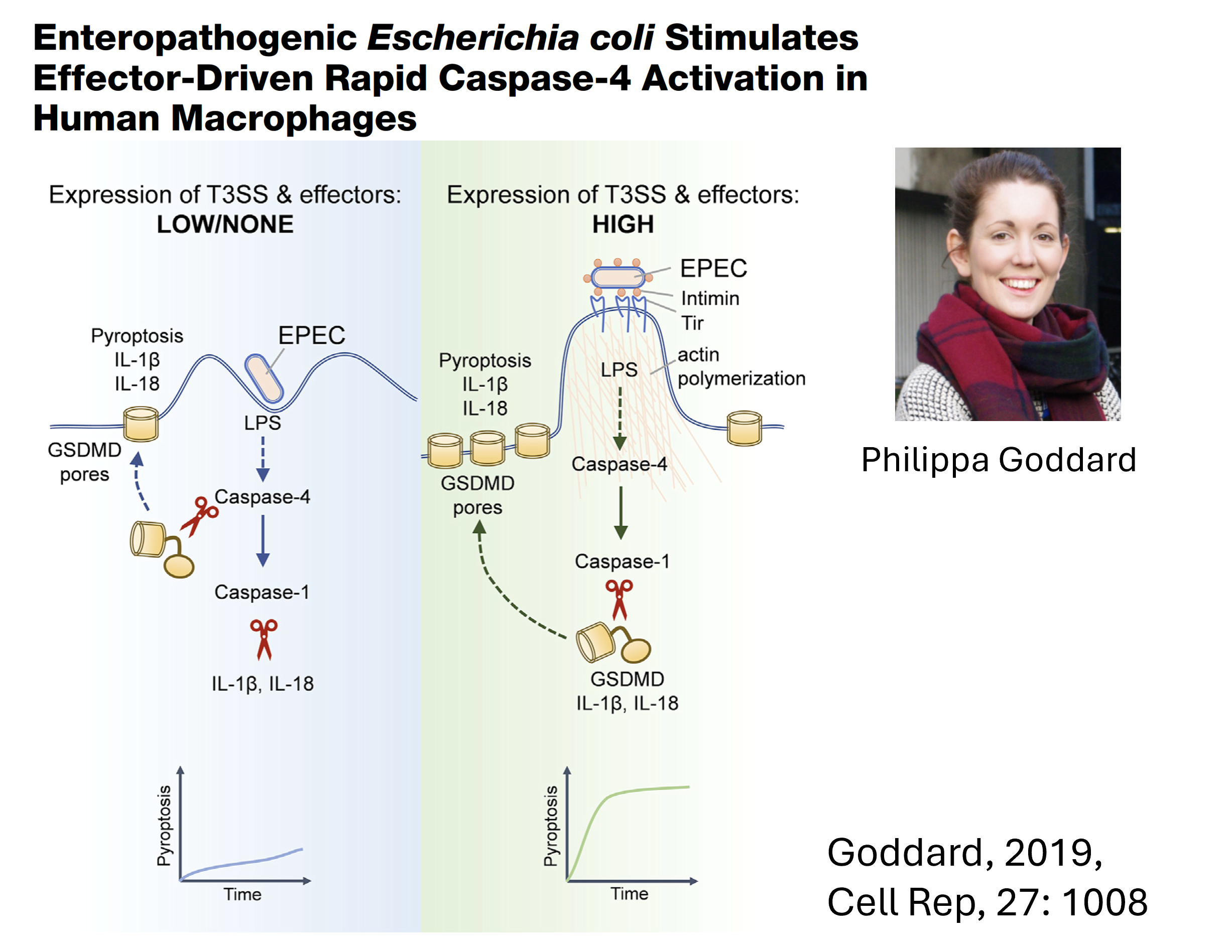
The pathogens we investigate are enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC), Salmonella and Shigella. We collaborate with wonderful colleagues on various aspects of work in this theme, including Eva-Maria Frickel, Gad Frankel, and Abigail Clements.